Kasen Zhai (Numega Nutrition Pte.Ltd, Singapore),
Theerawit Poeikhampha (Faculty of Agriculture, Kasetsart University, Thailand)
Since the European Union completely banned all antibiotics used in feed in 2006, formaldehyde has been approved to be used in feeds to ensure feed hygiene and safety. Formaldehyde plays an important role in achieving antibiotic-free in Europe. In particular, it plays an irreplaceable role in ensuring feed hygiene safety and avoiding cross-contamination in the process of feed production. According to a report by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA,2014), it shows that 0.2~1 kg formaldehyde per ton complete feed can effectively kill most harmful microorganisms. In addition, Wales AD etc., 2010 found that the use of formaldehyde can effectively control salmonella and other pathogens in feed and drinking water and minimize pathogenic microorganisms in the environment.
However, formaldehyde was banned to be used in feed in August 2018 based on the factors that is harmful to the human body. At the meantime, The EFSA recommends formic acid as an alternative to formaldehyde and approves its use in all animal species.
- Mode of action of formic acid against pathogenic bacteria
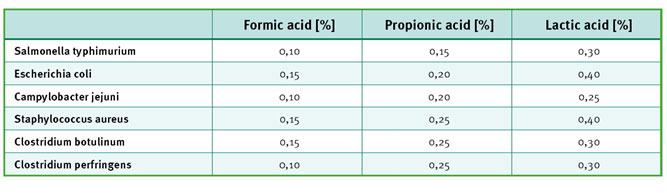
Formic acid is the smallest organic acid with the molecular formula is H2CO2, and the molecular weight is 46.03. Formic acid enters bacteria directly and efficiently in the form of acid molecules (pH≈7.0)(Figure 1),which liberate an anion(HCOO-) and a proton(H+) in the cytoplasm. This uses internal pH to decrease, a specific mechanism H+-ATP pump is activated, bring the pH inside the bacteria to a normal level. This phenomenon consumes many energies, can stop the growth of bacteria and kill it. In the meantime, carboxylate anions can inhibit the synthesis of DNA and proteins, so that bacteria cannot reproduce and achieve bactericidal effect (DIBNER J Etc., 2001). The results of comparing the bacteriostatic effects of different organic acids show that formic acid has a strong inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli and salmonella (STRAUSS G, 2001) (Table 2)
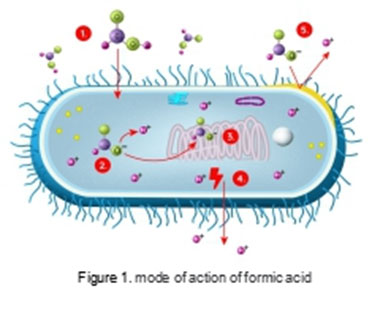
Table 2. Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of different organic acids (Strauss and Hayler2001)
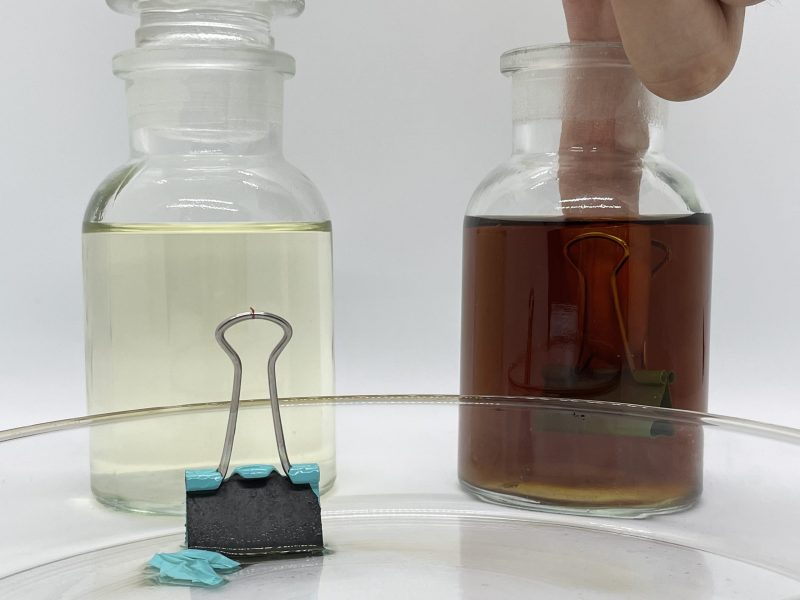
- Formic acid is corrosive and irritating
Formic acid has a strong irritating odor and corrosiveness, has strong irritation and damage to the eyes, respiratory tract and skin, and has strict requirements for transportation equipment and storage equipment. The EFSA also specified in the EU (EU) 2017/940 document that the maximum amount of formic acid used in complete feed is 1%. Therefore, the large-scale use of formic acid in animal husbandry has been greatly restricted. With the development of science and technology, non-stimulating and safe formic acid derivatives have been successively developed.
- Characteristic of diformic acid
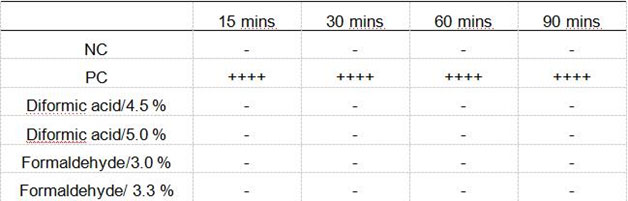
Diformic acid is a formic acid dimer formed by the polymerization of two formic acid molecules through van der Waals’force (VDW). It has a formic acid odor brown liquid and is also non-corrosive and non-irritating. The pH value of 1% diformic acid solution is about 2.5. Diformic acid releases two formic acid molecules against bacteria, and theoretically has the same mode of action with formic acid. The part of preliminary results showed that after 15 minutes of mixed culture of porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs) cells and African swine fever virus (ASFV), PAM cells were infected by the virus and Rosette appeared on the cell surface (Figure 3B). The Rosette on the surface of PAM cells disappeared 30 minutes after the addition of diformic acid at a concentration of 4.5 ml / L, and the virus was inactivated. At the same time, the study also found that the same effect can be achieved with the addition of formaldehyde at a concentration of 3 ml/L (see Table 4).
Table 4. Effects of different concentration of formaldehyde and diformic acid against ASFV in PAM cells
Conclusion
Formic acid has a strong bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, and has both the functions of acidification and nutrition. Under the trend of global animal husbandry’s non-resistance development, it has a very broad application prospect. However, the shortcomings of formic acid, such as its irritation and corrosiveness, have limited its use in large-scale production. Diformic acid not only weakens the defects of formic acid, but also completely retains the advantages of formic acid, reduces potential hazards to workers and equipment, and has the conditions for large-scale use.
Article published in Vietnam livestock magazine in April 2020
http://nhachannuoi.vn/don-doc-tap-chi-chan-nuoi-viet-nam-so-thang-4-2020/
http://nhachannuoi.vn/diformic-acid-thay-the-formadehyde-trong-cuoc-chien-chong-virus-asf/



